Yashvi Chheda
Bariatric Dietician & Content Writer

Bariatric Food Pyramid
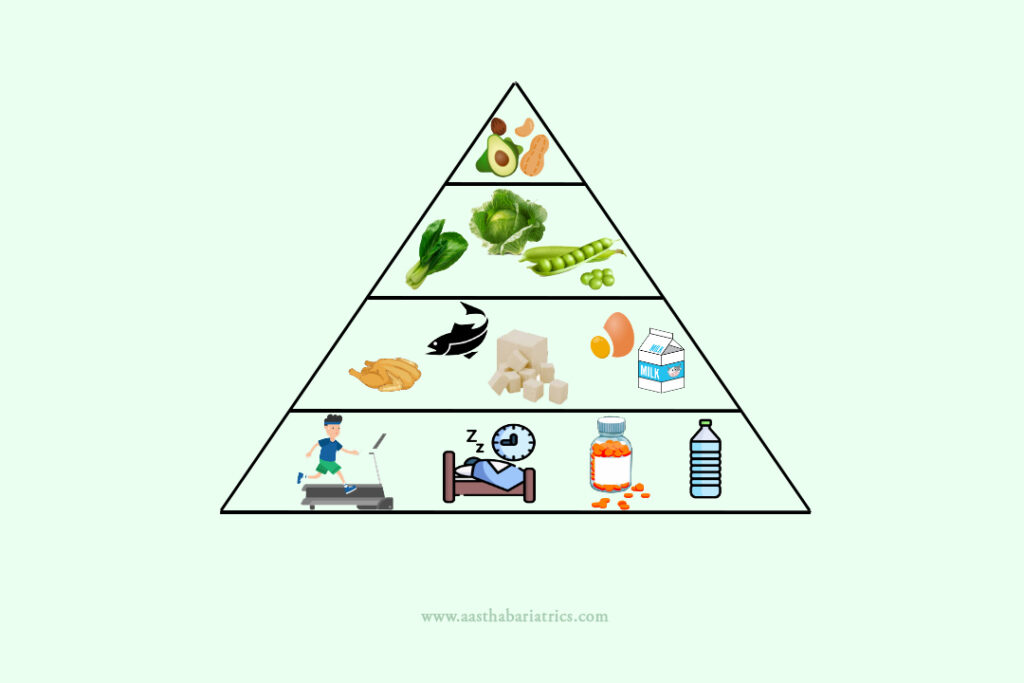

What is a food pyramid?
The food pyramid offers recommendations for healthy eating and serves as a graphic depiction of a balanced diet. It serves as an example of the various food groups and the suggested ratios for each category in a person’s daily diet. The idea that some food groups should be consumed in greater numbers while others should be consumed in lower quantities is better communicated by the pyramid design.
The food pyramid for people who have undergone bariatric surgery is different & includes lifestyle recommendations along with food. They have this different pyramid since they have varied amounts of requirements from each group.
The pyramid for them typically includes the following components, listed from bottom (largest portion) to the top (smallest portion).
The foundation for your new lifestyle should consist of exercise, sleep, supplements, and water.
Exercise: There is never an escape from exercise. Regular exercise increases calorie expenditure, which aids in weight loss and maintenance. Exercise can induce an energy deficit when accompanied with a healthy diet, which can result in moderate and long-lasting weight loss. Additionally, it can aid in avoiding weight gain following bariatric surgery.
By enhancing insulin sensitivity and lowering insulin resistance, exercise can enhance metabolic health. It can assist in controlling blood sugar levels and lowering the risk of type 2 diabetes, which is more common in obese people.
Exercise has been proved to improve mental health and general wellbeing. It can increase mood, elevate self-esteem, lessen signs of anxiety and despair, and generally improve quality of life. Bariatric patients may benefit from exercise in particular since it can help with improving body image and give them a sense of empowerment.
Sleep: Getting enough sleep is important for weight management and can affect your efforts to lose weight. Insufficient sleep has been linked to increased hunger, irregular eating habits, and cravings for items rich in calories. It can skew the ratio of hormones that control appetite, like ghrelin and leptin, increasing the likelihood of overeating or making poor food decisions. After bariatric surgery, getting enough sleep might help you maintain your weight and support healthy eating habits.
Bariatric patients should place a high priority on creating a consistent sleep schedule, a relaxing sleep environment, and good sleep hygiene in order to support healthy sleep habits. This entails staying away from stimulating activities right before bed, minimising screen time, maintaining darkness and silence in the bedroom, and controlling stress levels.
Supplements: Due to changes in their digestive systems and appetite control, bariatric patients often adhere to a limited diet and eat smaller portions. Due to this, it may be difficult to satisfy their nutritional demands merely through food consumption. By delivering concentrated forms of particular nutrients, supplements can fill up the gap and offer that people get enough of the necessary vitamins and minerals.
Significant weight loss and improvements in obesity-related health issues can result from bariatric surgery. However, maintaining these improvements and avoiding dietary deficits or problems requires long-term nutritional supervision. When recommended and utilised properly, supplements can help bariatric patients maintain their health over the long term.
Water: Everyone needs to stay hydrated, especially people who are overweight. Following bariatric surgery, the stomach’s capacity is reduced, leaving less space for food and liquids. To prevent dehydration and support different biological functions, it is even more important to maintain appropriate hydration.
Numerous bodily processes and systems, such as circulation, regulating body temperature, lubricating joints, and waste removal, depend on water. It lubricates joints, flushes out waste materials and poisons, and aids in the transportation of nutrients and oxygen throughout the body. For optimal physical performance and to maintain general health, it’s crucial to stay hydrated.
Proteins: Aim for 60-80g of lean protein each day. Example- tofu, eggs, beans, fish, chicken, etc.
Protein is crucial for bariatric patients for a number of reasons, including:-
Bariatric surgery frequently causes significant weight loss, which may include both lean muscle mass and fat mass. A sufficient protein intake aids in maintaining muscle mass, promoting muscle repair, and preventing muscle atrophy. This is crucial for maintaining a greater metabolic rate, strength, and general physical function.
Bariatric surgery causes tissue stress and incisions that need to heal properly. Protein is necessary for wound healing and tissue repair. The generation of new cells and collagen is supported by an adequate protein diet, which also improves immune function and lowers the risk of problems connected to wound healing.
Protein-rich foods have a tendency to be more filling and can aid in promoting feelings of fullness and satisfaction. Bariatric patients might feel satiated with fewer quantities by including protein in their meals and snacks, which lowers their risk of overeating or consuming too many calories. This can help with weight loss and weight management initiatives.
Absorption of nutrients: Bariatric procedures like gastric bypass or gastric sleeve alter the digestive tract, which may have an impact on absorption of nutrients. Protein is essential for the assimilation of other nutrients, including calcium and iron. Making sure you have enough protein can help with overall nutrition absorption and stop deficits.
Protein contributes to metabolic health, which includes insulin sensitivity and glucose management. Patients who have undergone bariatric surgery may be more susceptible to metabolic diseases like type 2 diabetes and insulin resistance. Consuming enough protein can enhance insulin sensitivity, boost metabolic health overall, and assist control blood sugar levels.
Green leafy vegetables: Aim for 3-4 servings of vegetables each day such as dark green leafy vegetables- spinach, cabbage, broccoli, etc.
Green leafy vegetables are a great source of phytonutrients, vitamins, and minerals. They are a great option for bariatric patients who need to maximise their nutrient intake while controlling their calorie consumption because they are low in calories but high in nutrients. For overall health and wellbeing, these vegetables include vital elements like vitamin C, vitamin K, folate, iron, and calcium.
For bariatric patients, green leafy vegetables are a good source of dietary fibre. Fibre enhances gastrointestinal health by encouraging regular bowel movements, preventing constipation, and preventing diarrhoea. It also contributes to satiety, which is advantageous for controlling hunger and weight.
The water content of many green leafy plants is high, including lettuce, spinach, and kale. This can aid in hydration, particularly for bariatric patients who may need to drink fewer fluids overall due to having a smaller stomach. Vegetables high in water content can help with general hydration.
Healthy fats: 2 servings of healthy fats each day such as olive oil, coconut oil, avocado, nuts, olives, etc. is important.
Due to changes in the digestive tract, bariatric surgery may have an impact on how well fat-soluble vitamins (including vitamins A, D, E, and K) are absorbed. Consuming these vitamins with healthy fats might improve the body’s ability to absorb and use them. It is possible to promote optimal nutrition absorption and avoid shortages by including healthy fats in meals.
Healthy fats often have a greater fulfilling effect and can aid in fostering sensations of satiety and fullness. Bariatric patients may feel more content after meals if there are modest amounts of healthy fats present, which lowers their risk of overeating or snacking on junk food. For managing weight and maintaining long-term success following bariatric surgery, this can be especially helpful.