Yashvi Chheda
Bariatric Dietician & Content Writer

Obesity - The Biggest Threat To Mankind

According to the latest news by WHO, obesity is now considered a disease. Statistics show that by 2035, over 4 billion people will be obese, i.e., more than half of the world.
Obesity is characterized by an excessive buildup of body fat to the point where it may be harmful to a person’s health. The body mass index (BMI), which is determined as a person’s weight in kilograms divided by the square of their height in meters (BMI = weight in kg/(height in m)2), is commonly used to measure it.
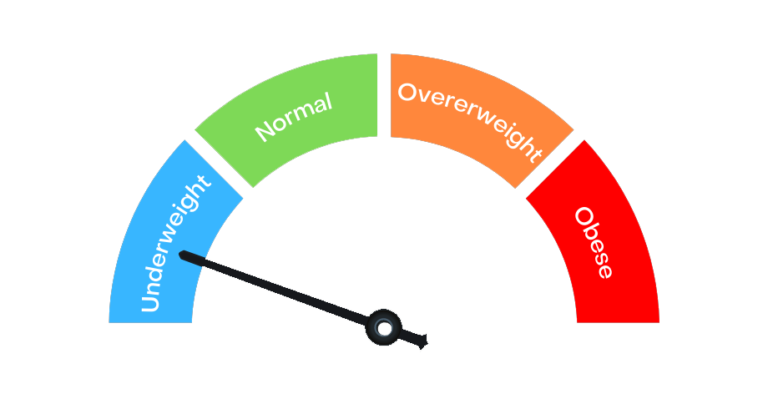
Weight is categorized as per BMI. Which is Body
Mass Index. It indicates the weight according to your height.
BMI categories:
Normal: 18.5-22.9 kg/m2
Overweight: 23-24.9 kg/m2
Obese grade I: 25-29.9 kg/m2
Obese grade II: 30-39.9 kg/m2
Obese grade III (Morbidly obese): 40-49.9 kg/m2
Super obese: >50 kg/m2
Combinations of genetic, environmental, and behavioral factors may contribute to obesity. Consuming high-calorie, unhealthy meals, living a sedentary lifestyle with little exercise, having specific medical disorders, hormone imbalances, heredity, and psychological factors are a few of the major causes.
Obesity is a big threat to mankind. It affects all parameters of life- physical as well as mental.
Here are a few explanations how:-
Affect on Mental Health:
Low self-esteem and body image problems: Obese people may have unfavourable body image impressions, which can lower their self-esteem and sense of worth. Feelings of guilt, embarrassment, and social isolation may emerge from this, which may worsen mental health issues.
Obesity is linked to an increased chance of having depression and anxiety disorders, including both. Feelings of pessimism, melancholy, and fear can result from the social stigma and prejudice experienced by obese people as well as the difficulties they have maintaining their weight.
Binge eating and emotional eating: Some people use food as a coping method to deal with stress, unpleasant feelings, or challenging circumstances. Emotional eating and binge eating can result in additional weight gain, feeding the obesity epidemic and having a detrimental effect on mental health.
Social isolation and loneliness: Because of the stigma associated with obesity, obese people may feel lonely and cut off from other people. Feelings of isolation and mental health problems may be exacerbated by this lack of social support.
Reduced quality of life: Obesity can impair physical mobility and cause health issues, which can lower someone’s quality of life in general. Distress and feelings of dissatisfaction may be a result of this diminished quality of life.
Reduced quality of life: Obesity can impair physical mobility and cause health issues, which can lower someone’s quality of life in general. Distress and feelings of dissatisfaction may be a result of this diminished quality of life.
Avoiding exercise: People who are obese may refrain from exercising because of discomfort, concern for others’ opinions, or a lack of confidence. Regular exercise plays a significant function in enhancing mood and lowering stress and anxiety in addition to being good for physical health.
Sleep disturbances: Sleep problems like sleep apnea are more likely to occur in people who are obese. Poor sleep can affect one’s mood, cognitive ability, and general mental health.
Affect on physical health:
Obesity leads to disastrous hormonal imbalance both in male and female, leading to various infertility disorders. In women it can lead to PCOS or anovulation which is no production of eggs. In men it can lead to impaired sperm production, reduced sperm quality, erectile dysfunction, etc.
Infertility in both men & women can lead to difficulty in conceiving and various other complications during pregnancy.
Obesity is a significant risk factor for coronary artery disease, heart attacks, and congestive heart failure, among other cardiovascular conditions. Unhealthy levels of body fat can cause cardiovascular issues such as high blood pressure, increased cholesterol, and inflammation.
Type 2 diabetes: There is a direct correlation between obesity and the development of type 2 diabetes. Insulin resistance and diabetes can result from the hormones and inflammatory compounds that adipose tissue (fat cells) secretes interfere with insulin’s capacity to control blood sugar.
Obesity hypoventilation syndrome (OHS), asthma, and sleep apnea are among breathing problems that obese people are more likely to have. These ailments may lead to weakened lung capacity and less oxygen consumption when you sleep.
Musculoskeletal issues: Being overweight puts more strain on joints, which can result in diseases like osteoarthritis. Obesity can impair mobility and produce chronic pain, making it difficult for people to participate in physical activity.
GI disorders: Gallbladder disease, gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) are all more likely to occur in obese people.
Obesity has been associated with an increased risk of acquiring a number of malignancies, including breast, colon, endometrial, kidney, and pancreatic cancer.
Obesity is a major risk factor for sleep disorders including sleep apnea, which can make existing health problems worse by preventing restorative sleep.
Stroke: Obesity raises the risk of stroke, a disorder in which blood flow to the brain is disrupted and may result in neurological deficits and probable brain damage.
If obesity is not treated, it can have serious consequences for physical health, including life-threatening consequences. The good news is that losing weight and changing to a healthier lifestyle can greatly lower the risk of these health issues.
In order to avoid and treat obesity-related health problems, bariatric surgery along with a balanced diet, frequent exercise, and obtaining competent medical guidance for weight management can all be quite helpful.
It’s crucial for people who are obese to have assistance from healthcare specialists to create individualized programmes for enhancing their physical and general well-being.