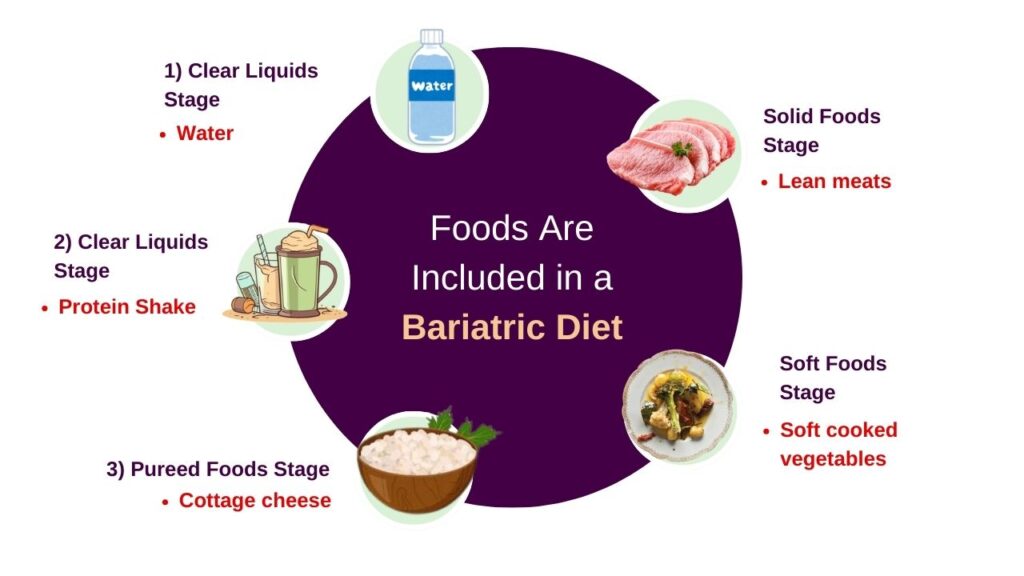
A Comprehensive Guide to What Foods Are Included in a Bariatric Diet
Introduction:
Embarking on a journey toward a healthier lifestyle through bariatric surgery necessitates not only a commitment to physical transformation but also a fundamental shift in dietary habits. Adopting a bariatric diet is important for achieving and maintaining weight loss while ensuring optimal nutrient intake. In this comprehensive guide, let’s look at the various types of foods that can be included in a bariatric diet.
Protein-Rich Foods: The Foundation of a Bariatric Diet
Protein is the cornerstone of a bariatric diet, playing a vital role in muscle preservation, wound healing, and overall metabolic function. Including lean protein sources in every meal is essential for post-surgery success. Opt for options such as:
Poultry: Skinless chicken and turkey are excellent sources of lean protein and eggs.
Fish: Fatty fish like salmon and trout provide omega-3 fatty acids alongside protein.
Lean Meats: Choose lean cuts of beef meet protein requirements without excess fat.
Vegetarian sources of protein include: Paneer, Tofu, soya chunks, all pulses and lentils
Dairy sources: Milk and milk products like curd, buttermilk, hung curd are all vegetarian sources of protein
Aim to consume protein at each meal, adjusting portion sizes to match individual dietary needs.
Non-Starchy Vegetables: The Nutrient Powerhouse -
Non-starchy vegetables are rich in essential vitamins, minerals, and fiber, making them an integral part of a bariatric diet. These foods contribute to satiety while providing vital nutrients without excess calories. Include a colorful array of:
Leafy Greens: Spinach, kale, and Swiss chard offer a nutrient-dense punch.
Cruciferous Vegetables: Broccoli, cauliflower, and Brussels sprouts add variety and nutritional value.
Colorful Veggies: Bell peppers, tomatoes, and carrots contribute antioxidants and flavor.
Varying vegetable choices ensures a broad spectrum of nutrients, promoting overall health and aiding in weight management.
Whole Grains: Balanced Carbohydrates for Energy -
While carbohydrates should be consumed in moderation, opting for whole grains provides sustained energy and essential nutrients. Whole grains are rich in fiber, promoting digestive health and aiding in weight loss. Incorporate:
Quinoa: A versatile and protein-rich grain.
Brown Rice: A wholesome alternative to white rice, offering fiber and nutrients.
Oats: A fiber-packed option for breakfast or snacks.
Whole grains contribute to a balanced diet, supporting long-term weight management and nutritional needs.
Low-Fat Dairy or Dairy Alternatives: Calcium for Bone Health -
Adequate calcium intake is crucial post-bariatric surgery to support bone health. Opt for low-fat or fat-free dairy products or suitable alternatives, such as:
Greek Yogurt: A protein-rich and probiotic-packed choice.
Skim Milk: A calcium source with reduced fat content.
Almond or Soy Milk: Dairy-free alternatives fortified with calcium.
Including these options ensures a sufficient calcium intake, especially when combined with other dairy or calcium-rich foods.
Fruits in Moderation: Natural Sweetness and Essential Nutrients -
While fruits contain natural sugars, they also offer essential vitamins, minerals, and fiber. Moderation is key to managing carbohydrate intake. Incorporate:
Berries: Rich in antioxidants and lower in sugar compared to some other fruits.
Apples and Pears: Fibrous options providing a satisfying crunch.
Citrus Fruits: Oranges, grapefruits, and lemons contribute vitamin C.
Enjoying fruits in moderation adds variety and essential nutrients without compromising weight loss goals.
Healthy Fats: Essential for Nutrient Absorption -
Including sources of healthy fats is vital for nutrient absorption and overall well-being. Opt for unsaturated fats found in:
Avocado: A nutrient-dense source of monounsaturated fats.
Nuts and Seeds: Almonds, walnuts, and chia seeds provide healthy fats and protein.
Olive Oil: A versatile oil rich in monounsaturated fats.
Incorporating these healthy fats supports the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins and contributes to overall nutritional balance.
Hydration: Water, Water, Water -
Staying adequately hydrated is paramount in a bariatric diet. Water not only supports digestion but also helps prevent dehydration, which can be common after surgery. Aim to consume at least eight glasses of water daily and avoid sugary or high-calorie beverages.
Additionally, herbal teas and infused water with citrus or herbs can add flavor without unnecessary calories.
A bariatric diet is not a one-size-fits-all approach; it requires individualization based on specific needs, preferences, and surgical procedures. Consulting with a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian specializing in bariatric nutrition is essential to create a personalized and sustainable eating plan.
As individuals navigate the post-bariatric journey, the inclusion of protein-rich foods, non-starchy vegetables, whole grains, low-fat dairy or alternatives, fruits in moderation, healthy fats, and consistent hydration sets the foundation for success. Balancing these food groups ensures a diverse range of nutrients, promoting optimal health while supporting weight loss and maintenance.
Remember, adopting a bariatric diet is important for your health and well-being. It’s about nourishing the body with nutrient-dense foods, making mindful choices, and fostering a positive relationship with food. With the right guidance and a thoughtful approach, individuals can embrace this dietary transformation as a key element in their journey toward a healthier and more fulfilling life.
Read also; The Cost of Bariatric Surgery in India
Why We Are?
- Asia's Trusted Bariatric Center
- Centre of Excellence
- Patient Trusted Highly Volume Bariatric Center in Mumbai
- EMI, Cashless & Mediclaim Facilities are Available
- Daily Patients Follow-up after Bariatric Surgery
- Patient Support Group Every Month
- Obesity Awareness Program
- Available with Latest Technologies
- 18+ Experience in Weight Loss Bariatric Surgery
- 300+ Weight Loss Diet Plan & Recipes
- Highly Trained & Experienced Bariatric Nutritionist
- Patient WhatsApp Chat Group
- & Many More
Medically reviewed by Dr. Manish Motwani, Bariatric & Metabolic Laparoscopic Bariatric Surgeon — Curated by Akansha Mishra