Mubashira
Bariatric Dietician & Content Writer
Bariatric Surgery After Cancer: How It Has Reduced Risks & Improved Outcomes
Impact of Bariatric Surgery on Obesity and Cancer
Bariatric surgery aims at major weight loss and is performed on patients who are obese or morbidly obese. Bariatric surgeries make significant changes to the digestive system and the treatment aims to treat obesity and help people lose weight. Along with this can also lead to remission or reduction in the symptoms of various obesity-related issues such diabetes, hypertension, sleep apnea, knee pains, high cholesterol, heart diseases, PCOS, etc.
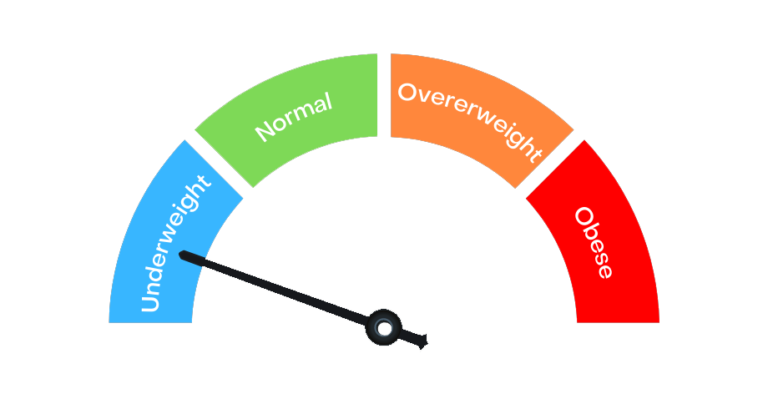
Healthcare providers commonly use the Body Mass Index (BMI) to define obesity in the general population. The BMI measures average body weight against average body height. As a generalisation, healthcare providers associate a BMI of 30 or higher with obesity. There are three general classes of obesity that healthcare providers use to evaluate what treatments may work best for each person. They include:
Less than 30 cat…..
Class I obesity: BMI 30 to <35 kg/m².
Class II obesity: BMI 35 to <40 kg/m².
Class III obesity: BMI 40+ kg/m².
Obesity has become a global epidemic with a soaring economic encumbrance due to its related morbidity and mortality. Amongst obesity-related conditions, cancer is indeed the most redoubtable. Bariatric surgery has been proven to be the most effective treatment for obesity and its associated metabolic and cardiovascular disorders.
Obesity promotes and accelerates cancer development and growth by multiple mechanisms. While adipose tissue was once considered to simply provide storage for energy rich lipid reserves, to be released in time of energy needs, it has become clear it can actually function as a mediator of multiple metabolic and inflammatory signals. Expanding adipose tissue contributes to increased circulating adipokines, including leptin, retinol binding protein, resistin and visfatin, each of which has been shown to stimulate tumour growth. Obesity also increases chronic inflammation in the
body, which is thought to lead to chronic stress in cells and, eventually, damage to DNA. This can elevate the risk of cancer.
Figure A - female
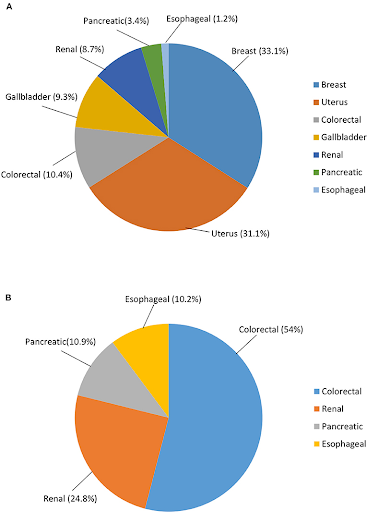
Figure B - Male
Cancer risk worldwide attributable to overweight and obesity, according to gender.
The International Agency for Research on Cancer has recently identified 13 malignancies with sufficient evidence for them to be identified as obesity associated cancers (OACs). These OACs include post-menopausal breast, colorectal, kidney, endometrial, thyroid, pancreas, liver, gastric cardia, meningioma, ovary, esophageal adenocarcinoma, gall bladder and myeloma.
When the researchers looked at the risk reduction by type of surgery, the two types used most commonly today, gastric bypass and sleeve gastrectomy, were both associated with a reduction in overall cancer risk.
Type of bariatric surgery | How it works |
Roux-en-Y gastric bypass | The surgeon places staples in the stomach, creating a small pouch in the upper section. The stapling makes the stomach much smaller, so the person eats less because they feel full sooner. In addition, part of the small intestine is divided and attached directly to the small stomach pouch. Because food will bypass most of the stomach and the upper part of the small intestine, the body will absorb fewer calories. |
Sleeve gastrectomy | The surgeon removes most of the stomach, leaving only a banana-shaped section that is closed with staples. The surgery reduces the amount of food that can fit in the stomach, making the person feel full sooner. |
Based on the magnitude of benefit shown, weight loss surgery can be considered in addition to other interventions that can help prevent cancer and reduce mortality. Further research needs to be done to understand the underlying mechanisms responsible for reduced cancer risk following bariatric surgery.