Bariatric Surgery for type 2 diabetes - Aastha Bariatrics
Medically reviewed by Dr. Manish Motwani, Bariatric & Metabolic Laparoscopic Bariatric Surgeon — Curated by Aditi Apurva
Table of Contents
The chronic health condition, in which the body accumulates excess fat over time, is none other than the obesity, leading to a gradual increase in body weight. Blame the positive energy balance in the body! Which happens when the calorie intake is more than what the body actually spends? Other reasons for obesity include lack of sleep, sedentary lifestyle, and metabolic disorders like hypothyroidism, genetics and family history. Body Mass Index (BMI) is a tool used to determine if a person is obese.
What is Diabetes Mellitus?
It is a metabolic disorder characterized by the decreased ability or complete inability of the tissues to utilize carbohydrates, accompanied by change in the metabolism of fat, protein, water and electrolytes. The disorder is due to a deficiency or diminished effectiveness of the hormone insulin.
There are major 2 Types of Diabetes Mellitus seen among people, Type 1 and Type 2.
Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus
This usually affects overweight and obese adults. The insulin production maybe normal, however, the insulin produced is not as effective as normal insulin. The symptoms of diabetes are gradual and slowly progresses with time.

Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
This usually affects overweight and obese adults. The insulin production maybe normal, however, the insulin produced is not as effective as normal insulin. The symptoms of diabetes are gradual and slowly progresses with time.
Other types of diabetes are
Malnutrition-related Diabetes Mellitus
It occurs in young people between 15-30 years of age. Generally people with MRDM are lean and undernourished. In this type of diabetes, the pancreas fails to produce adequate insulin.
Gestational Diabetes Mellitus
It is diagnosed when glucose intolerance is detected for the first time during pregnancy. It is often diagnosed during 2nd or 3rd trimester due to insulin resistance caused by the rise in insulin antagonist hormones.
How does it work on obesity and hence cure Type 2 diabetes mellitus?
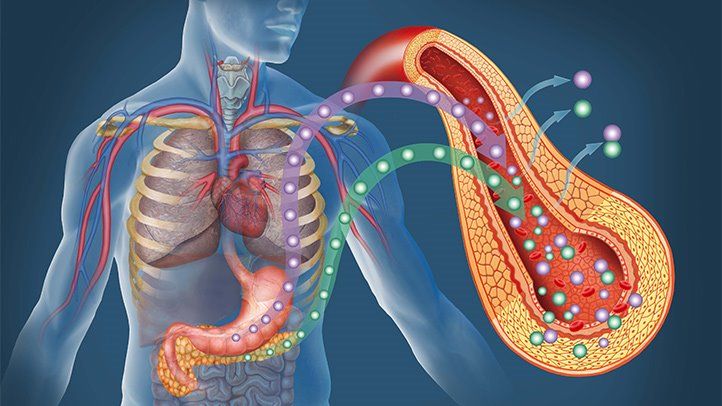
Extra fat accumulated around the waist, means fat can build up around our vital organs like liver and pancreas. The excess fats leads the pancreas to not functioning normally, it leads to insulin resistance.
Beta cells are unique cells in the pancreas that produce, store and release the hormone insulin.
Abdominal fat can increase the risk of pancreatitis, which can cause beta cell dysfunction.
Removal of this fat can make insulin work better because pancreas began to work better and is able to keep up with our body’s need for insulin.
Therefore, weight loss helps maintaining the blood sugar levels.
Bariatric surgery or Weight Loss Surgery
Weight loss surgery or fat removal surgery is collectively known as bariatric surgery and works by altering the digestive system. It is the most effective on-going treatment for obesity and its associated metabolic complications. It is performed when diet and exercise have not worked for long duration and the risk of having serious health complications are high due to obesity or being overweight.
It can be restrictive or malabsorptive or both.
In malabsorptive, the physiology of the human digestive system is altered that leads to changes in the chemical processes of digestion. Physiological alterations after the surgery result in malabsorption causing the body to generate lesser energy. To overcome the energy deficit, fat stored in the body is broken down and gets depleted over time.
In restrictive, the capacity of the stomach decreases. So, we tend to consume lesser quantity of food, and eat only as much as is needed. This helps in curing several lifestyle diseases and prevents the individual from gaining weight over and over again.
Medically reviewed by Dr. Manish Motwani, Bariatric & Metabolic Laparoscopic Bariatric Surgeon — Curated by Kaushal